Working with Ableton Link
With the help of Carabiner, Triggers can synchronize an Ableton Link session’s tempo, beats, and bars to the track playing on their watched player, or you can add Link as its own “player” that can become Tempo Master to the CDJs. Even without Carabiner, you can control which players are Synced, and which is the Tempo Master.
Overview
If you install and run Carabiner, Beat Link Trigger can tie into an Ableton Link session, so you can synchronize programs like Ableton Live, Traktor, and an increasing collection of others (as well as more and more hardware), to the tempo and beat grid established by the players being watched by your triggers.
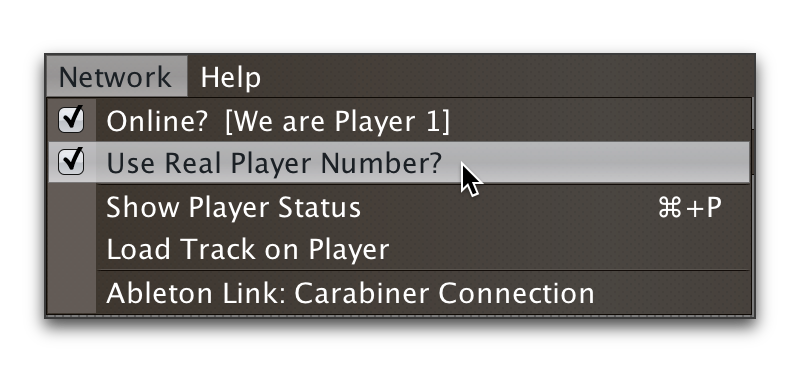
Once you have installed Carabiner and have it running, bring up the
Carabiner Connection window by choosing
Ableton Link: Carabiner Connection in the Network menu:
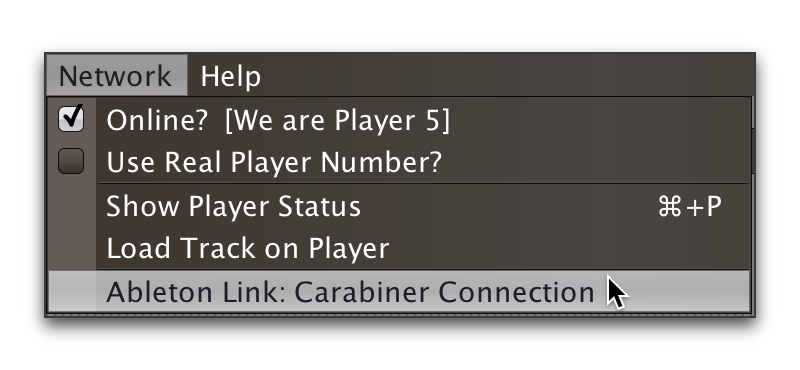
This will open the Carabiner Connection window (the set of devices you see at the bottom will depend on what is actually on your network):
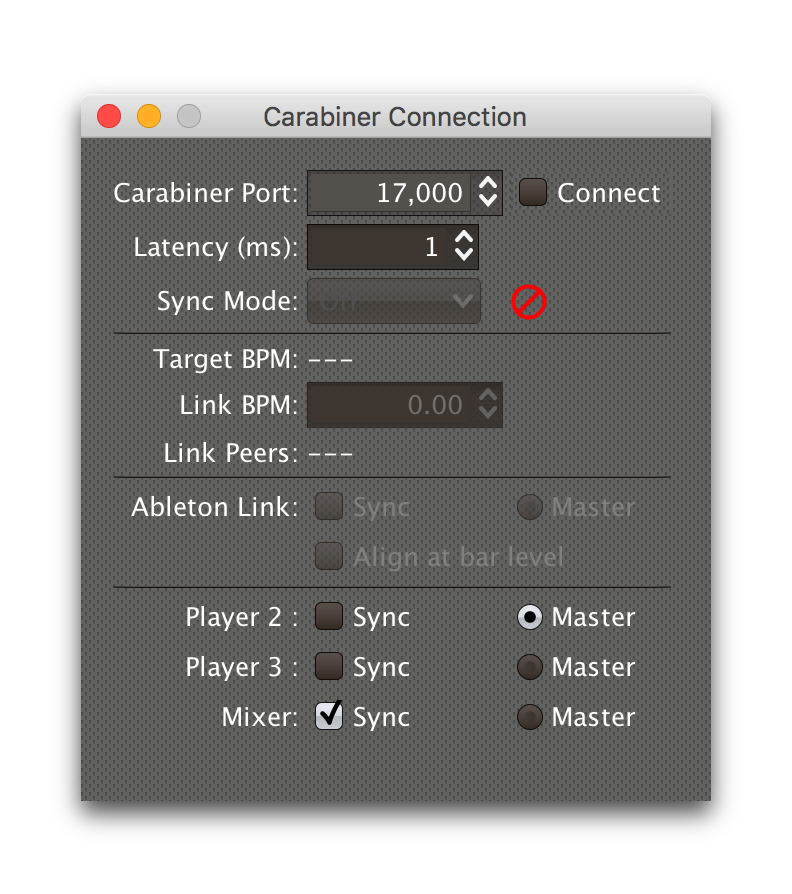
This window will also open whenever you choose Link in a
trigger’s Message Menu, or load a trigger
that is configured that way, if Carabiner is not already connected.
|
Set the Carabiner Port value to match the port on which your
Carabiner daemon is listening. The default value of 17000 will work
unless you have had to explicitly tell it to use a different port
because some other program is using that one on your system.
The Latency value is the number of milliseconds it takes from when a
beat is actually playing on the players in your DJ Link Pro network to
when the corresponding beat packet is received by Beat Link Trigger.
The default value of 1 ms seems to work well, but if your Ableton
Link session seems to be running audibly behind beats from your
Pioneer gear, you can increase this value until things sound right.
Once your port value is correct, you can click the Connect check box to establish a connection with Carabiner:
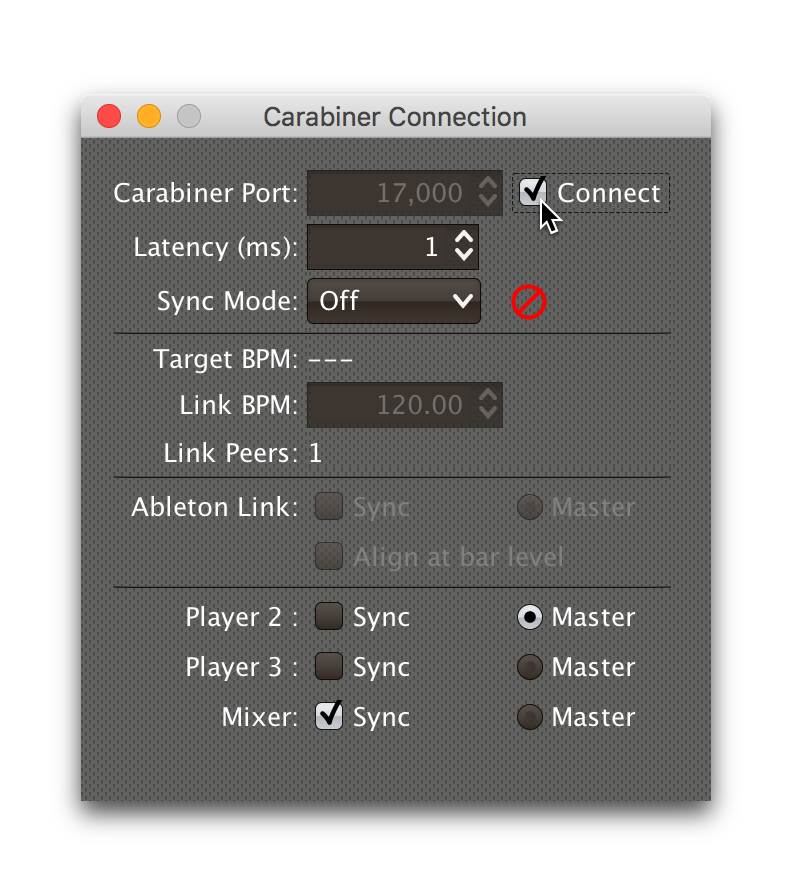
Once connected, you can no longer adjust the port value, but you can tweak the latency at any time while listening to sound from your Pioneer gear and Link-enabled software or hardware.
The current tempo of the Link session is shown, as well as the number of other Link-enabled programs (Link Peers) visible on the network.
Syncing with Triggers
In order to allow triggers to influence the Link session, configure a trigger to send to Link by choosing in the trigger itself:
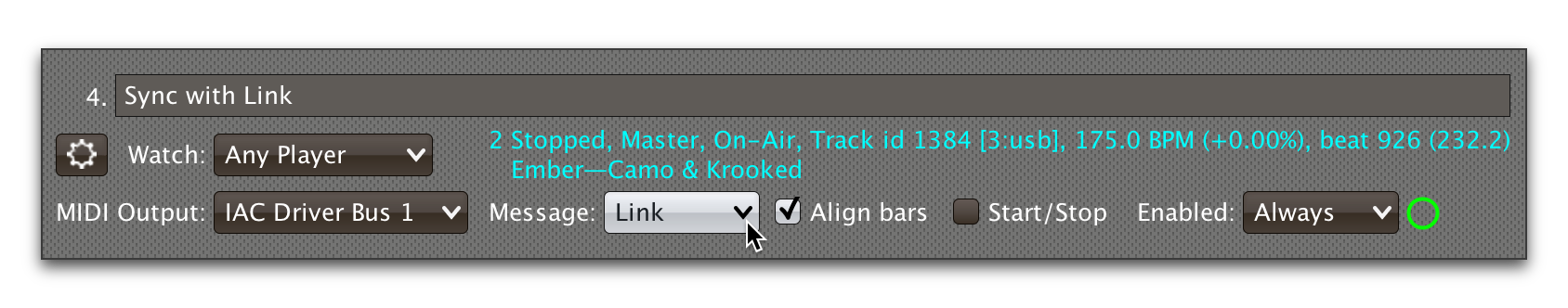
Triggers that work with Link can align the beat grid with either
individual beats, or entire bars of four beats (the default). If you
want simple beat-level alignment, uncheck the trigger’s Align bars
check box.
If the systems you are integrating with support version 3 of the
Ableton Link protocol, you can also use its Transport Control feature
to tell them to start playing when the trigger activates, and stop
when it deactivates, by checking the trigger’s Start/Stop checkbox.
Software and devices using older versions of the protocol will simply
ignore these instructions even if you have this turned on.
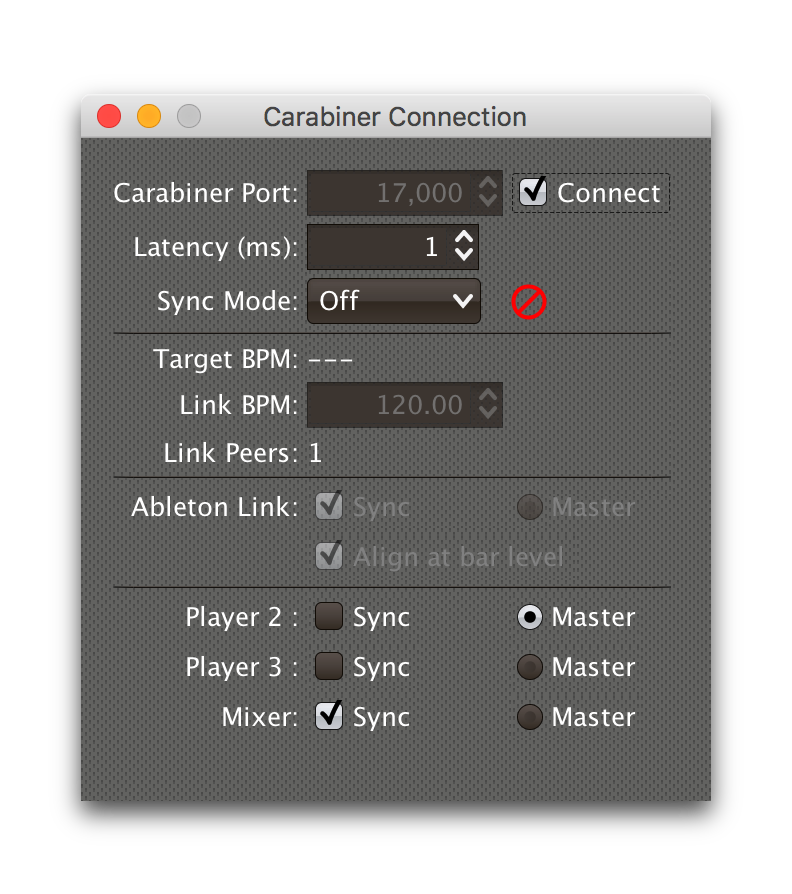
Once a trigger like this activates, the tempo of its watched player
will show up as the Target BPM within the Carabiner Connection
window. That is not happening yet, though:
Starting with version 0.4.0 of Beat Link Trigger, Carabiner can sync without using triggers at all. If you still want to use it in that mode, you need to choose in the Carabiner window. Once Carabiner is connected and set to Triggers as its Sync Mode, whenever a Link trigger is active, Beat Link Trigger will control the Link session tempo, and will align it to the beat (or bar) of the trigger’s watched player:
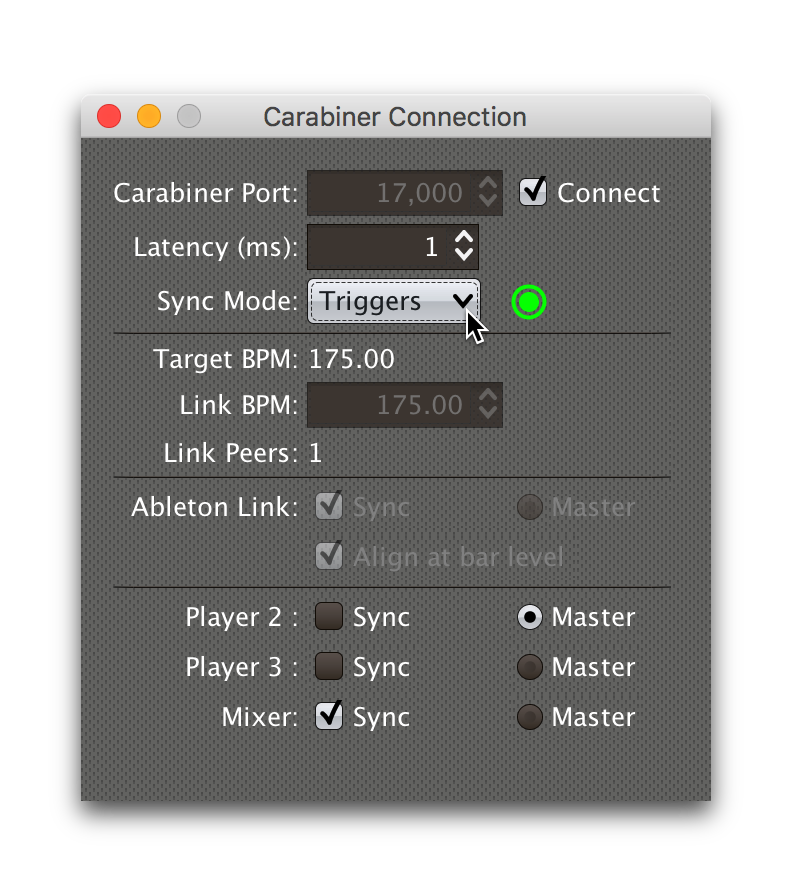
Carabiner Status (Triggers Mode)
To the right of the Sync Mode menu there is a status indicator
which shows whether Carabiner is currently enabled (a green circle) or
disabled (a red circle with a slash). To be enabled, the Connect
check box must be checked and the Sync Mode menu must be set to
something other than Off.
When you are using Triggers as your Sync mode, if a Link trigger is currently active and thus trying to affect the Link session, there is a filled circle inside the enabled circle:
| State | Indicator |
|---|---|
Disabled (Sync Mode |
|
Enabled, No Link Trigger Active |
|
Enabled, Link Trigger Active |
|
Passive Sync Mode
Sometimes you simply want to tie the Ableton Link session to whatever
is playing on the CDJs, without having to set up a trigger to manage
it. You can do that by choosing in the
Carabiner window. As soon as you do that the Ableton Link section of
the window becomes enabled:
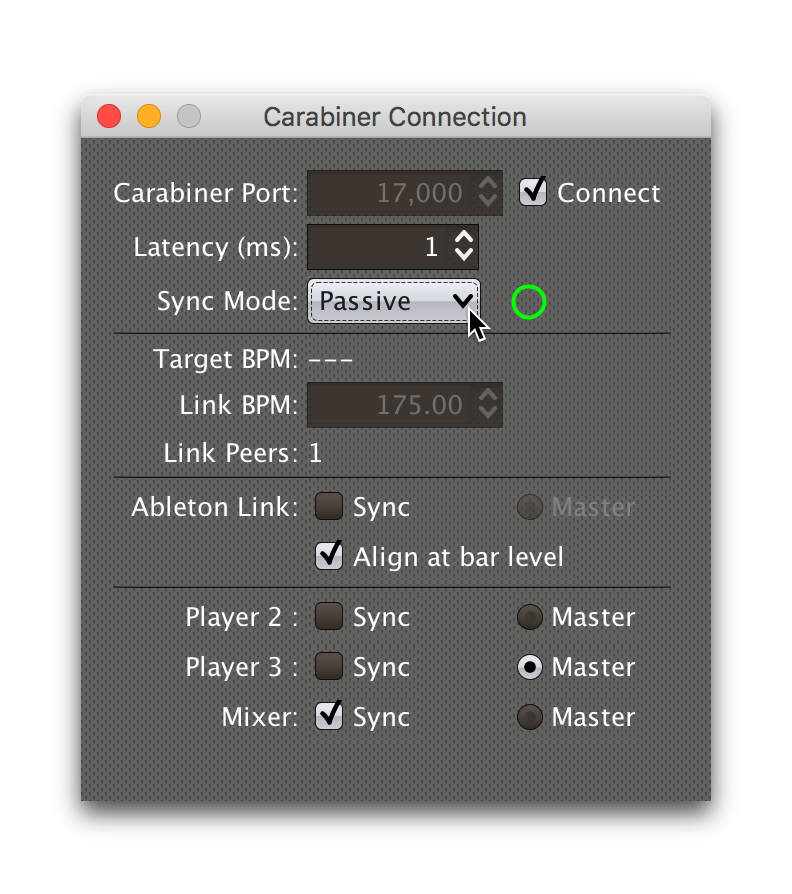
This gives you a place to control the things that a trigger would
normally set for you (whether the Link session is currently being
synced, and if it should be aligned at the level of beats or entire
four-beat bars). Since it starts out with Sync unchecked, when you
are ready to tie the Link session to the Pioneer beat grid, simply
check the Sync checkbox in the Ableton Link section:
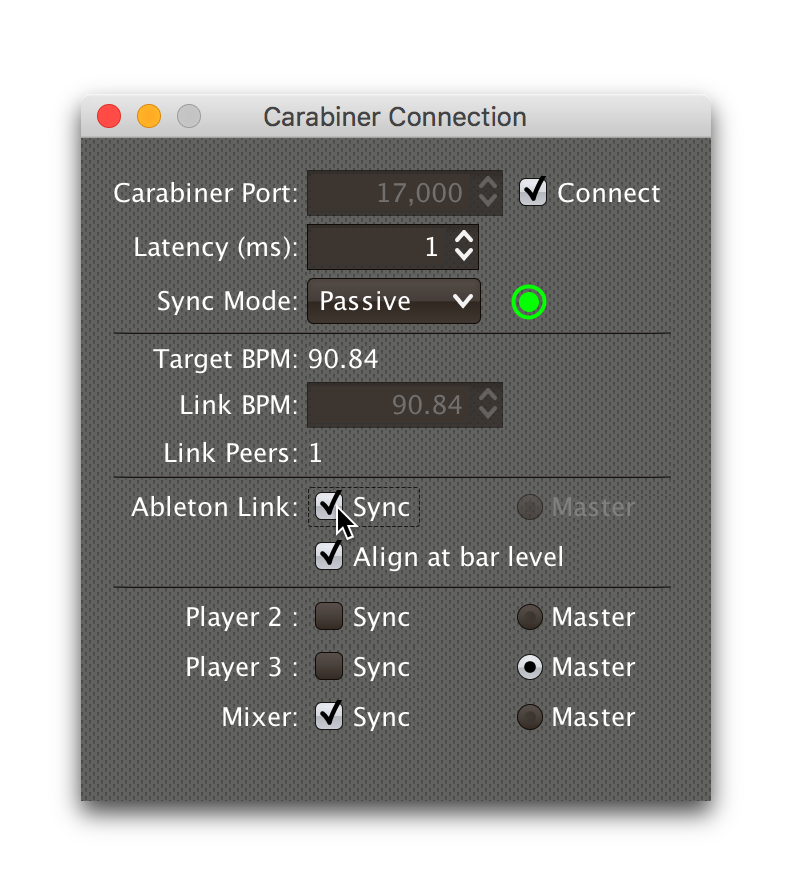
At this point the Link session will follow the master Pioneer player, until you change the Carabiner settings.
|
If you are using Passive or Full Sync Mode, and
would still like a trigger to control the Ableton Link transport
(playing/stopped) state, you can do it by calling functions in your
trigger expressions. Use
You do need to make sure Carabiner is connected before calling either of these functions, though. This will do the trick: (when (beat-link-trigger.carabiner/active?) ;; Your code here ) If you want to only start or stop the transport when the |
Carabiner Status (Passive Sync Mode)
The Sync Mode status indicator works very similarly in this mode to
how it worked in Triggers mode, except that it doesn’t depend on the
state of any triggers. If the Sync checkbox is checked, it shows
an active Sync state:
| State | Indicator |
|---|---|
Enabled, Not Synced |
|
Enabled, Synced |
|
The Sync checkbox works for the Link session in the same way the
device Sync checkboxes in the bottom section do for Pioneer devices,
as described in the Sync Control section below. This
Sync Mode is called Passive because Ableton Link can only follow the
Pionner players, it can never control their tempo or beat grid. That
is why the Master radio button in the Ableton Link session remains
disabled. To enable that, you need to take the Sync Mode all the way
up to Full, which is our next topic.
Full Sync Mode
If you want the Ableton Link session to be a full participant on the Pioneer network, and able to become Tempo Master, choose in the Carabiner window.
|
In order to do this, Beat Link must be using a standard player number, so it can fully participate as a Tempo Master. You turn this on by checking .
|
Once you successfully activate Full Sync Mode, the entire Ableton Link section is enabled, and you can have the Link session become Tempo Master for the Pioneer players by clicking the Master radio button in that section:
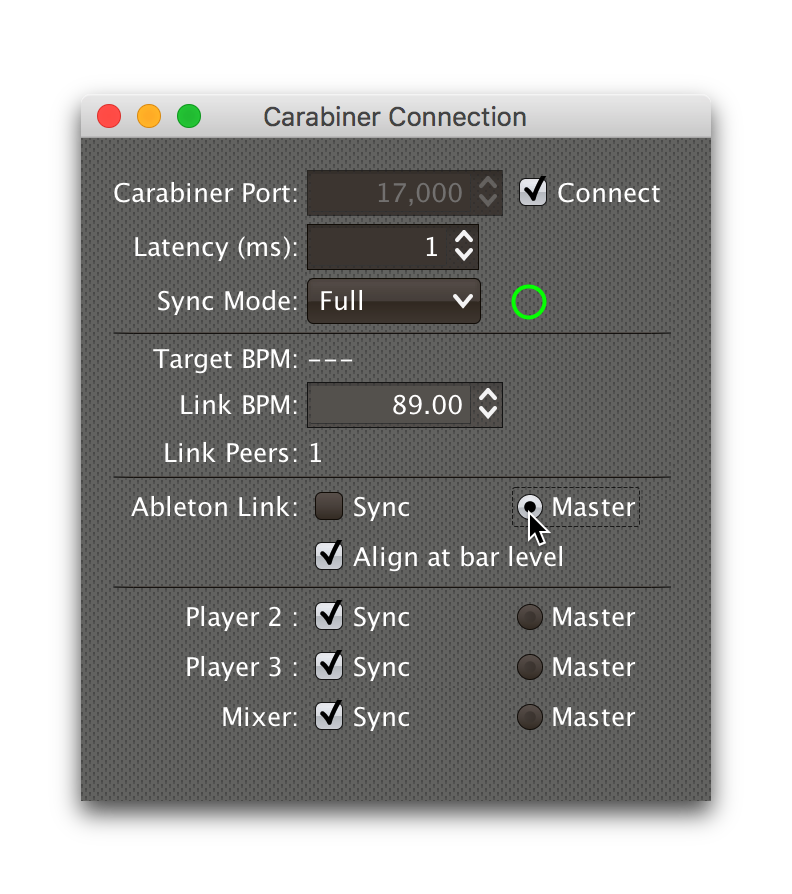
When Link is tempo master, any Ableton Link enabled software or hardware can control the Link session tempo, and any Pioneer players that are in Sync mode will follow along, aligning to the beats (or bars, if you have that option checked) of the Link timeline.
In this Sync Mode, the Link BPM becomes editable in this window as
well. You can click on the arrows to nudge it up or down by 0.01 BPM
at a time, or you can type a new tempo in the field and press
Return to jump immediately to that tempo. This will affect both
the Link session itself, and any Pioneer players that are in Sync
mode.
Carabiner Status (Full Sync Mode)
The Sync Mode status indicator again works similarly in this mode to
how it worked in Passive Sync mode, except that it shows an active
Sync state when either the Ableton Link Sync checkbox is checked or
its Master radio button is chosen.
| State | Indicator |
|---|---|
Enabled, Neither Synced nor Master |
|
Enabled, Synced or Master |
|
You can also put any player in Sync mode, or assign it as the Tempo Master, which is the topic of the next section.
Player Sync Control
The bottom section of the window lets you see and control which players are in Sync mode, and which is the Tempo Master.
| You can use this feature without connecting to Carabiner, and without even installing the Carabiner daemon. |
Simply check or uncheck the Sync checkbox to adjust each player’s
Sync state, or click the Master radio button of the player that you
want to become the Tempo Master.
Beat Link’s implementation of the sync control protocol works in both directions. If the DJ causes another player to become Tempo Master, the Link session will gracefully give up that role. The checkboxes and radio buttons will update to reflect any changes made on the players themselves. And if there is a DJM mixer on the network, it can tell Beat Link to turn its own Sync on or off, or become Tempo Master, and Beat Link will obey.
Connecting Automatically
If you would like to automatically connect to Carabiner and set up sync when you bring Beat Link Trigger online (because you know it is running in an environment where Carabiner will always be running), you can accomplish this using the Came Online Expression, and there is an example of how to do this in the description of that expression.
Other Automation
The example shown in the Came Online Expression illustrates that the Carabiner Connection window is designed for convenient use by your custom expression code. Here is a list of functions that you can call.
Player Sync Control Functions
This first set of functions can be used without opening the Carabiner Connection window, and do not even require a Carabiner daemon to be installed or running. (Beat Link Trigger does need to be Online, though, and the device numbers you mention do need to be on the network, or an exception will be thrown, terminating your expression.)
To check the Sync status of a Pioneer device, call sync-device and
pass in the player number. If you have a Nexus mixer, it will use
player number 33. This is how you would check the Sync status of
player 2:
(beat-link-trigger.carabiner/sync-device 2)The result of that call will be true if the player is currently in
Sync mode, or false otherwise. So you can use it as part of an if
or when construct to control what the rest of your expression does.
To change the Sync state of a player, pass a second argument, using
true to turn Sync on, and false to turn it off. So putting player
1 in Sync mode would be achieved like this:
(beat-link-trigger.carabiner/sync-device 1 true)Similarly, to check whether a player is currently Tempo Master, you
can call master-device with its player number:
(beat-link-trigger.carabiner/master-device 3)The result of that call will be true if the player is currently the
Tempo Master, or false otherwise. To assign a new Tempo Master, you
call appoint-master-device with the player number that you want to
take over the Tempo Master role:
(beat-link-trigger.carabiner/appoint-master-device 2)Carabiner Control Functions
The remaining functions in this section can only be invoked when the
Carabiner window has been created, which you can do by calling
show-window:
(beat-link-trigger.carabiner/show-window nil)The second argument can be a window that you want to center the
Carabiner window on top of, but most expressions will not need to do
that, and so will simply pass nil.
Once the window has been created, you also need to connect to the Carabiner daemon before anything else can work, which you can do as follows (but you will need to be sure that you always have a Carabiner daemon running if you are writing code like this):
(beat-link-trigger.carabiner/connect)Once connected to Carabiner, you can choose a sync mode by calling
sync-mode. With no arguments, it will return the current mode. To
set a mode, pass a keyword argument with the value :off, :trigger,
:passive or :full, which will turn Carabiner sync off, or set it
to Triggers, Passive, or
Full mode.
(beat-link-trigger.carabiner/sync-mode :full)| You need to be in Full sync mode to be able to control the tempo of the Pioneer network based on the Ableton Link session tempo, and Beat Link Trigger needs to be using a standard player number in order to enter Full sync mode. |
When sync between Ableton Link and the DJ Link network is enabled, it
can be performed at either the level of individual beats, or of entire
bars (measures). The function align-bars can check or control this
setting. To align the networks at the level of bars of music, you
call:
(beat-link-trigger.carabiner/align-bars true)Passing a false argument turns off bar-level alignment, and passing
no argument returns the current setting.
To control whether the Ableton Link tempo is currently being tied to
the DJ Link network, you use the sync-link function. With no
arguments, it returns the current sync state. Passing a true
argument ties the Ableton Link session tempo to follow the DJ Link
Tempo Master.
(beat-link-trigger.carabiner/sync-link true)Passing a false argument frees Ableton Link to manage its tempo
separately.
If Carabiner is in Full sync mode, you can also have the Ableton Link
session tempo act as the Tempo Master for the Pioneer network. To
activate that, call appoint-ableton-master:
(beat-link-trigger.carabiner/appoint-ableton-master)There are no arguments to this function. If you want to check whether the Ableton Link session is currently the Tempo Master, you call:
(beat-link-trigger.carabiner/master-ableton)This will return true if the DJ Link network is currently seeing the
Ableton Link session as the Tempo Master, and false otherwise.
Ignoring Track BPM
In very special situations, for example when you want to synchronize with a set of Ableton tracks that have not been properly tempo marked or warped, but are all pretending to be at 120 BPM, you can tell Beat Link Trigger to ignore the actual tempo of the track that is playing on a CDJ, and adjust your fixed tempo value based on the current playback pitch.
To do this, use the Global Setup Expression to assign a value to the
:use-fixed-sync-bpm global, like so:
(swap! globals assoc :use-fixed-sync-bpm 120.0)Once you have done that, Beat Link Trigger will pretend that whatever track is playing has a native tempo of 120 beats per minute (or whatever value you have chosen). If the DJ plays it at a pitch of +5%, Beat Link Trigger will sync the Link session (or MIDI clock, which also supports this setting) to 126 BPM (which is 5% more than 120), regardless of the actual tempo of the track.
| This fixed Sync BPM override works only for Trigger-driven sync, and works for triggers configured to use either Link or MIDI Clock. It has no effect when you are using the Carabiner window in Passive or Full Sync mode to bridge the Ableton Link session to the Pioneer network. |
Don’t forget you have done this, or you will wonder why your sync is not working properly when you are trying to sync with tracks and systems that are properly beat gridded and tempo analyzed! To get back to normal, either remove the above line from your Global Setup Expression and quit and restart Beat Link Trigger, or edit the expression and replace that line with the following one, which undoes the setting immediately:
(swap! globals dissoc :use-fixed-sync-bpm)License
 Copyright © 2016–2019 Deep Symmetry, LLC
Copyright © 2016–2019 Deep Symmetry, LLC
Distributed under the Eclipse Public License 1.0, the same as Clojure. By using this software in any fashion, you are agreeing to be bound by the terms of this license. You must not remove this notice, or any other, from this software. A copy of the license can be found in LICENSE within this project.
Library Licenses
Remote Tea, used for communicating with the NFSv2 servers on players, is licensed under the GNU Library General Public License, version 2.
The Kaitai Struct Java runtime, used for parsing rekordbox exports and media analysis files, is licensed under the MIT License.